VarSome's CNV classifier explained
Charles Chapple, PhD, VarSome's Head of Bioinformatics, demonstrates the power of VarSome's automated implementation of ACMG guidelines for CNV interpretation.
In a collaboration with HPST, VarSome and Agilent distributor for the Czech Republic, we evaluate a solution for the detection of exon-level CNVs by sequencing of Agilent target enrichment libraries followed by analysis in VarSome Clinical.
Charles Chapple, PhD, VarSome's Head of Bioinformatics, demonstrates the power of VarSome's automated implementation of ACMG guidelines for CNV interpretation.
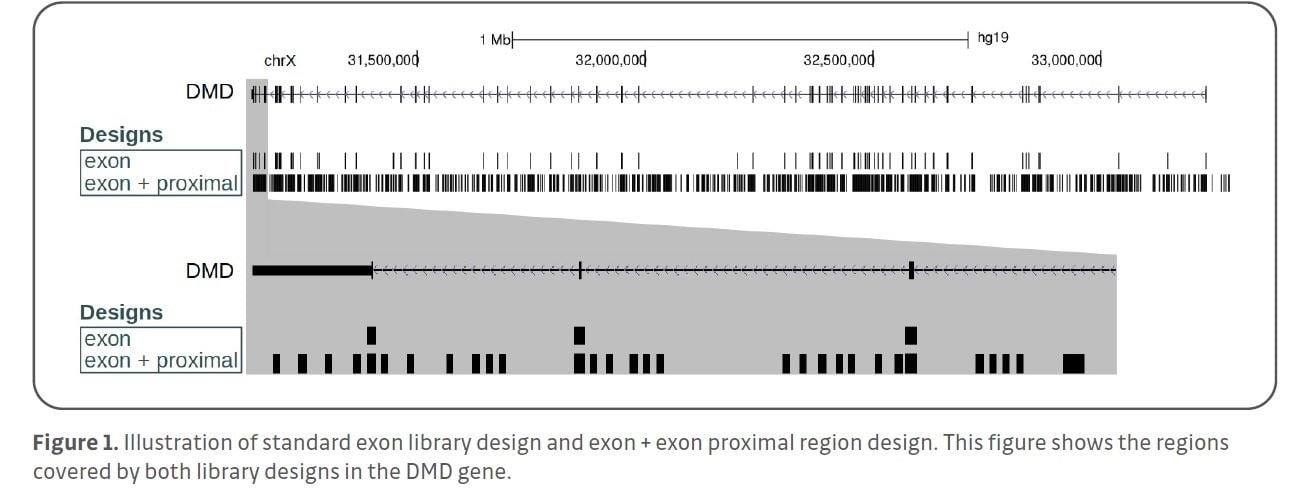
In addition to short variants, targeted sequencing can also be used to detect CNVs. This is usually performed by read depth analysis assuming that the number of sequenced DNA fragments is proportional to the copy number of a particular genomic locus. This approach is inaccurate in cases of small CNVs spanning only few or even a single exon. Target enrichment library designs developed by Agilent Technologies provide a solution to overcome this limitation by the inclusion of so-called “exon-proximal regions”.
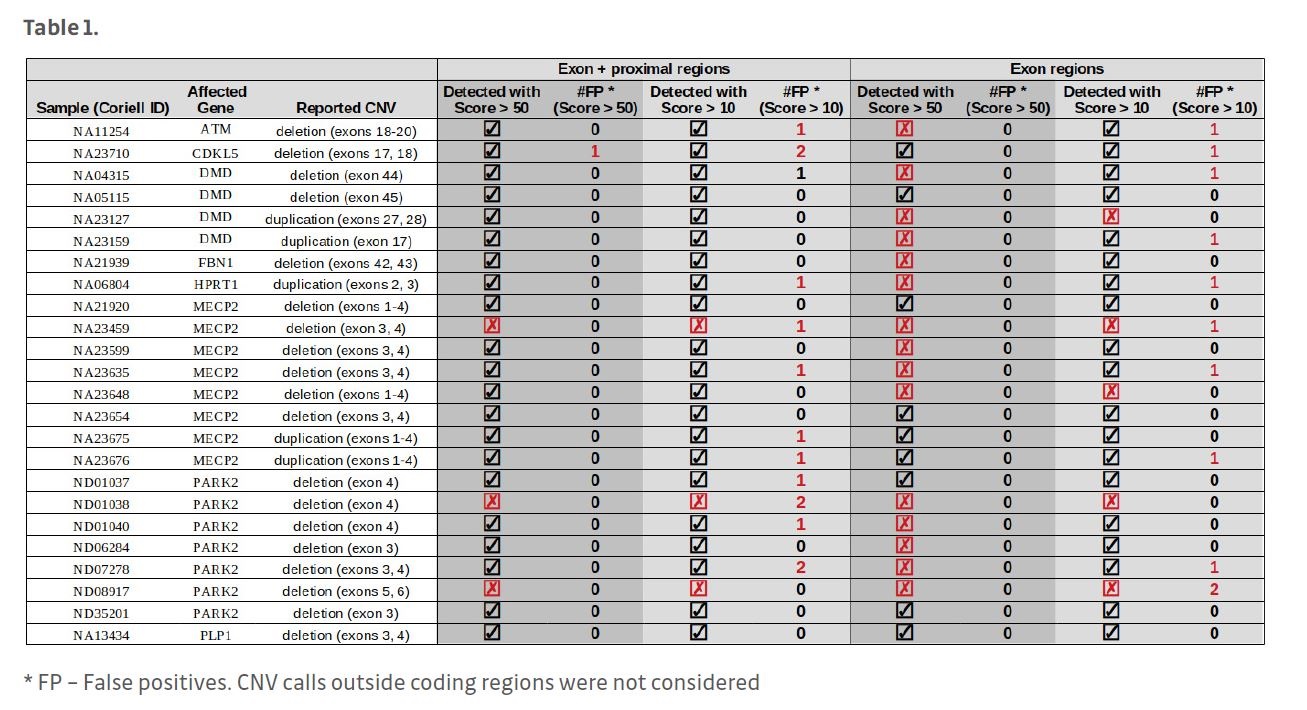
NGS libraries were generated using Agilent SureSelect hybridization-based target enrichment technology. Twenty-four Coriell Institute reference samples were sequenced on Illumina HiSeq2000.
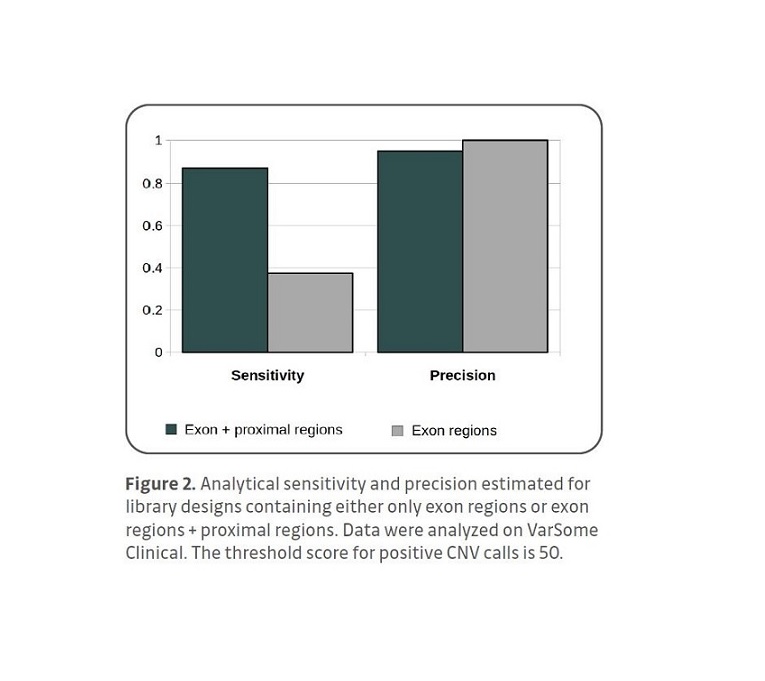
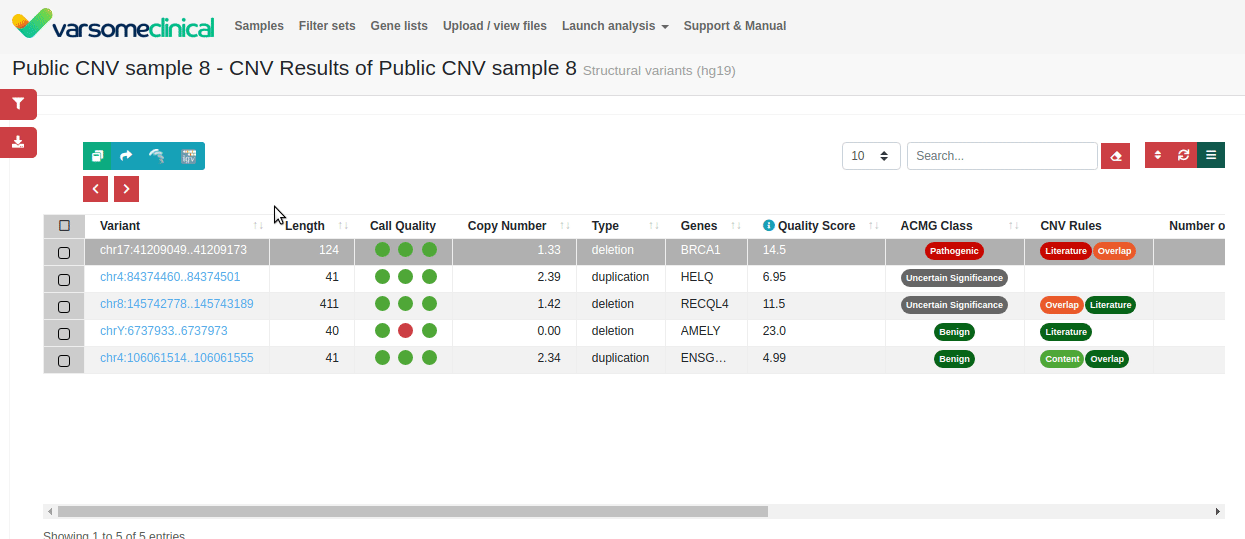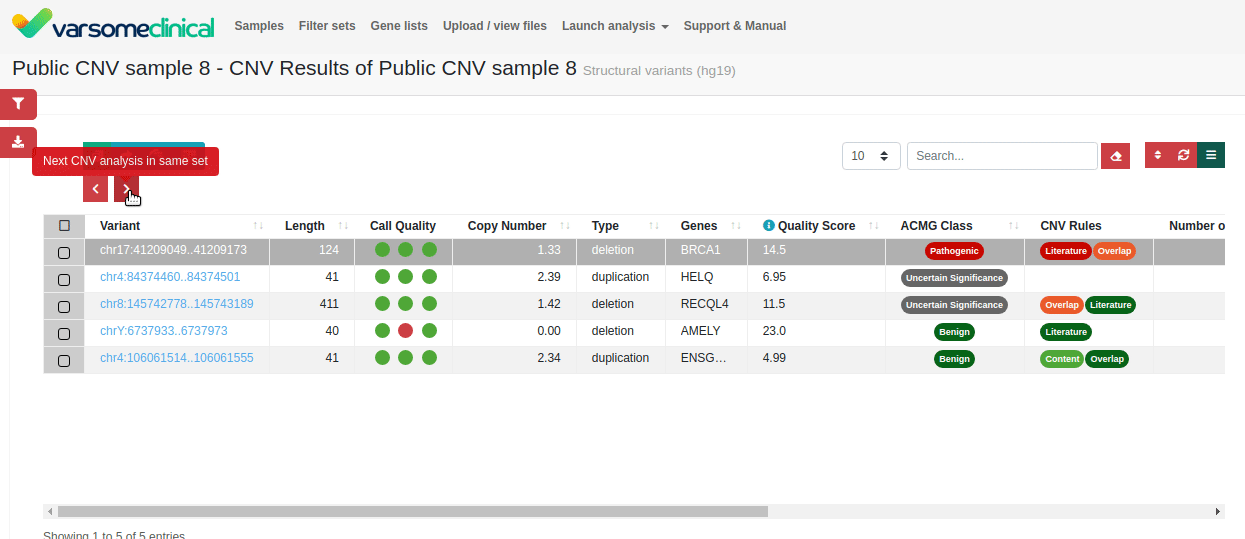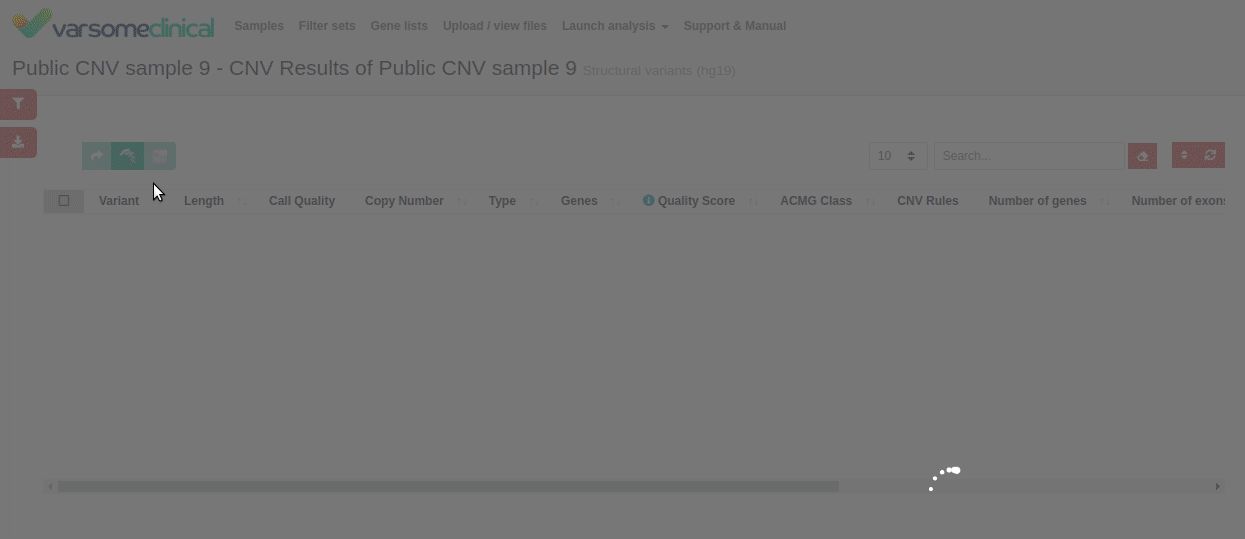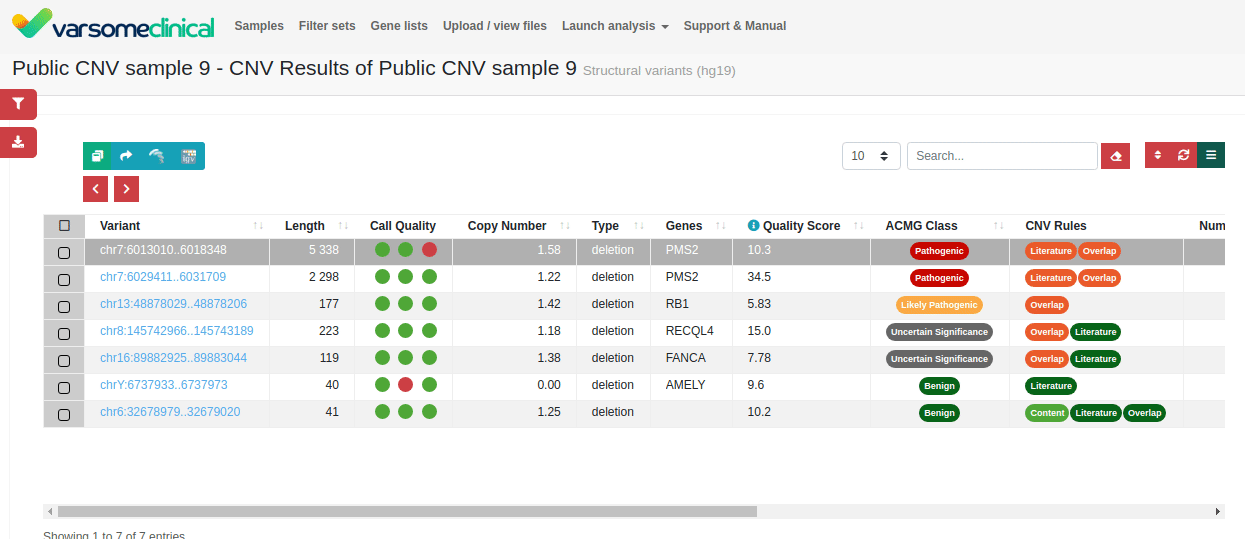
Analysis of exon-proximal region libraries in
VarSome Clinical enables robust exon-level
CNV detection. Exon-proximal regions increase the accuracy of CNV breakpoint assignment. The intuitive interface of VarSome Clinical enables easy inspection of individual CNV calls.
Since publishing this application note, we have added a new CNV Classification tool to help you apply ACMG variant interpretation criteria to your samples. Find out more here or contact us to schedule a demo.
VarSome Suite is brought to you by Saphetor SA.
© 2024 Saphetor SA – All Rights Reserved.